vimatics
vi medicine informatics
Deck Step1 All Subjects
by
1. Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9
- aka PCSK9!
- increases degradation of Hepatic LDL receptors –> Inc uptake of LDL into liver –> Decreased LDL serum
- alirocumab, eva …?
2. C-Peptide Halflife?
- 35 mins
3. Iatrogenic Complication: Thyroid surgery
- Hypocalcemia (hypoparathyroidism) –> Chovestek sign
4. ATP-Sensitive K Channel (k-ATP channel)
- ATP binds to channel causing K influx –> release of Insulin
5. ADominant Hereditary Hypothalamic Diabetes Insipidus
- Point Mutation in Neurophysin II
6. TRH stimulates the release of both:
- TSH
- PROLACTIN
7. DOPAMINE —(-)—> PROLACTIN
8. Osteoprotegrin: Decoy binder for RANK-Ligand
- PTH reduces OPG –> Increased RANK-L –(+)–> RANK binding –> Activation of Osteoclasts –> Inc calcium resoprtion –> Inc serum Ca+
9. Teriparatide: PTH analogue
- Intermittent use: Bone formation
- Continued use: Bone resorption, osteoporosis
10. Site of PTH action?
- PCT: PTH –(-)—> Na/PO4 cotransporter –> Excretes PO4
- DCT: PTH –(+)—> Na/Ca Exchanger –> Reabsorpbs Ca
11. FGF-23: Released in Response to HyperPhosphatemia
- Analogue of PTH
- Reduces 1alphaHydroxylase –> decrease Calcitriol
- produced by OSTEOCYTES
- Earliast Marker of HyperPhosphatemia
- Needtoverify: downregulation of NPT gene reduces PO4 absorption

12. Intermittent PTH/Analogue use?
- Greater proportion of Osteoblastic activity vs Osteoclastic activity
13. PTH Action
-
PTH –> receptor on Osteoblasts –> Activation –> Inc production of RANK-L and Monocyte Colony Stimulating Factor
-
PTH: Inc RANK-L & Inc M-CSF & Dec OPG-decoy
14. Hepatic Gluconeogenesis Inhibited by?
- Sepsis
- Beta Blockers
- Cytokines
15. Insulin Sensitivity is Decreased in CKD
- due to high metabolites & UREA
16. Syndrome: Disorientation, sweating, palpitation
- Hypoglycemia
17. Glut4
- skeletal muscle
- adipose tissue
- excercise increases glut4 (AMP, Calcium Calmodulin Kinase Protein Modulator)
- Insulin increases glut4 (dependent)
18. Prophylactic Erythromycin to Newborns
- prevent Opthalmia neonatorum by N. Gonorrhea
- else leads to blindness
19. Advanced Directive Types:
- Living will
- hospital proxy
20. Elizabeth Model for Grief: (stages)
- Denial
- Anger
- Bargaining
- Depression
- Acceptance
Syndrome: Facial grimmacing, lip-smacking, Tongue movements and puckering
- Tardive diskinesia
- s/e: Typical antipsychotics
- months to years after starting the drug
- Rx: change (clozapine), venlabenzine, deutrabenazine
Learning Disorders
- academic disorder, difficulty in – Learning – Reading – Writing
Boderline Personality Disorder
- Unstable relationships
- Mood instability
- libaility
ATP7B Mutation?
- Wilson
- ARecessive
- too much Ca
ATP7A Mutation?
- defective Cu absorption
- Too less Calcium
Deposits in Descemet membrane of Cornea?
- Keyser-Fleischer Rings
- Wilson
Failure to meet age related expectations in multiple areas, including intellctual, communicative, social and motor functions
- Global development Disorder
Engage in time-consuming, repetative behavior (mirror checking, excessive grooming) causing significant impairment in functioning:
- Body dysmorphic disorder
Ziprasidone:
- QT Interval
- ECG Monitoring
- SGA-Psych
Risperidone:
- Prolactin Elevation – Hypogonadism – Osteoporosis – Galactorrhea – Amennorhea
FLAT EFFECT
- Schizophrenia
Low Melatonin in CSF
- Alzeimers disease
Reversible acute confusional state with reduced or fluctuating level of consciencess
- DELIRIUM
Competitive Athletes, dancers fashion models
- Functional Amenorrhea
SIADH: SSRIs!
- Carbamazepine
- Cyclophosphamide
- SSRI
Decreased Cortisol:
- Hypoglycemia
- Normocytemic Anemia
- Eosinophilia
Magnocellular neurons:
- Suprooptic/paraventricular N of Hypothalamus
- ADH/Oxytocin
Bradycardia and Hypo/Hypertension in Hypothyrodism?
- HypErtension
Bilateral Fetal Hydronephrosis in Boys
- Posterior Urethral valve defect
Principle: Oxygen-induced Hypercapnia in COPD
COPD patients given oxygen will become lethargic, seizures due to O2 induced hypovent.
Already chronic C02 retainers –> “compensated” Respiratory Acidosis! Alterations in V/Q balance in lungs can increase deadspace ventilation and further rise in PaCO2
-
At baseline: – Pulmonary vasoconstriction: diverted to well ventilated areas of the lung – Chronic Hypoxic state: High Hgb affinity for CO2 – Peripheral chemoreceptor stimulation
-
After O2 administration – Vasodilation diverts blood away from well ventilated regions – Decrease Hgb affinity for CO2 (Haldane effect) – Decreased chemoreceptor stimulation
-
Effect – Increase Physiologic dead space (V/Q mismatch) – Increase Blood PCO2 – Decrease Minute Ventilation
Ranke Complex
- Fibrosed Ghon complex
- lower lobe infection
- ipsilateral lymph node
PO2 Content
- Mixed with pulmonary shunt blood

ENOLASE
- GLycolysis
- 2Phosphoglycerate —[enolase]–> PEP
Poison Ivy, oac, sumac
- Urshiol induced dermatitis
- contact dermatitis
Problems in Proteosomes:
- More viral infections!
- intracellular viral degradation initiation
- Ubiquitin tags proteins to be degradaded
Valsalva Maneuver –> Decrease Venous return
- Bearing down, forceful exhalation
Valsalva –> Loud Murmer in ?
- Loud in HOCM
- Decreasing LVFilling –> Increase LV Outflow tract Obstruction (worsens) –> Murmer loud!
Valsalva –> Softer Murmur in ?
- Soft in AS
- Decrease LV Filling –> Decrease LVEDP –> less gradient, softer murmer
HOCM Murmur
- Anything that reduces Preload –> Increase Murmur intensity
- Anything that increases Afterload –> Decrease Murmur intensity
POST MI, continued High CK
- Reperfusion injury –> O2 radical damage to cell wall by neutrophils –> CK release from BRAIN/HEART/Muscle
Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II or BMPR2 is a serine/threonine receptor kinase
- BMPR2
- Connective tissue disease, HIV infection
AR, MR, VSD murmurs increase when __load increases?
- Afterload increases
- handgrip, squatting
Exercise induced fatigue, pain parasthesias or dizziness and vertigo:
- SUBCLAVIAN STEAL SYNDROME
- severe stenosis of proximal subclavian artery –> reversal in blood flow from contralateral vertebral artery to ipsilateral verterbral artery
- ARM ISCHEMIA in affected EXTREMITY
EF Formula:?
Ef = SV / EDV
SV = EDV - ESV
Ef = EDV - ESV / EDV
Normal > 50%
54. Meds for Chronic Heart Failure with reduced EF (CHFrEF)
- Mortality benefit: – ACE – ARB – Nephrilisin INhib (CI with ACE == angioedema) – Beta blocker : metaprolol – Spironolactone (specially for Pulmonary Edema)
- No Mortality Benefit: – Diuretics – Digoxin reduces hospitalization
55. features of HF with Preserved EF
- In Diastolic Dysfunction: EF could be preserved over >50
-
56. Formation of Atheroma:
- Endothelial dysfunction
- Cholesterol, HDL, LDL goes into the intima –> monocytes migrate (Macs) –> phaogcytoze LDL become foam cells –> produce growth factors –> collage synthesis in intima, smooth muscle proliferation, extracellular necrotic debri
57. Internal carotid artery derived from which arch?
- Pharyngeal arch 3: Common Carotid and Proximal-ICA
58. Eccentric Ventricular Enlargement, CO is high/low/normal?
- CO is maintained.
- LV systolic dysfunction –> LV vent enlargement –> FRANKSTARLING –> SV Maintained –> [YEARS LATER: CHRONIC] –> Cardiac remodelling –> Sarcomeres added in Series to accomodate Inc LV Volume –> Eccentric Hypertrophy –> SV Still maintained –> [DECADE LATER] –> cannot compensate anymore incoming fluid –> Contractile Dysfunction –> Decompensated Heart Failure
- CO eventually falls
59. Breast Milk does not contained Vitamin ….. and ……?
- K and D
60. B12 absorbed from? and how?
- b12 is absorbed in ILium, its got to survive the stomach acidity!
- Helped by R-protein and IF
- b12-protein complex in stomach, R-binder from salivary gland also in stomach –> Stomach acdity separates b12 from protein and binds R-binder –> goes into Duodenum –> Pancreatic Protease splits R from b12 –> IntrinsicFactor (IF) binds b12 –> b12-IF complex absorbed form ILIUM
61. INDIA INK?
- Basically detects GELATINOUS capsule
- ENCAPSULATED budding yeast
- Cryptococcus Neophhh???
62. VHL tumors in renal, adrenal medulla and ..?
- Cerebellar & Retinal hemangioblastomas
63. How big are lacunar infarts?
- < 15 mm cavity infarcts
64. Microbes causing COPD exacerbation?
Dyspnea and/or cough, Changes in Sputum color Physical: PURSED LIPS with prolonged expiration
- Viral – Rhinovirus – Influenza – Parainfluenza
- Bacteria – H. Infl, Moraxella catarrhalis, Strep Pneumonia
- Airpoultion, embolism
65. IPP becomes equal/greater/less than Airway pressure in Emphysema?
- Greater than airways
66. Bleomycin sideeffect: causes __ due to __?
- Pulmonary fibrosis due to Free radical formation
67. Phthirus Pubis… LICE!
68. Superior Messenteric artery is usually at ……. angle?
- 45; pathologic if less < 20
- compresses 3rd part of duodenum if < 20 degrees
69. Fetal Hb begins production ….
- By 8 weeks
70. Extremely high affinity for O2?
- 4 gamma chains in Hb
- Hb Barts
71. Leading cause of Foodborne gastroenteritis?
- Campylobacter jejuni (which is also implicated in Guillain barre syndrome)
72. Sudain III Stain identifies what in Stool?
- Fat!
73. Most severly affected nutrient in malasoprtion: FAT!
74. Generalized Malabsorption causing conditions:
- Defective pancreatic secretiosn
- muscosal disorders - Celiac, IBD (crohn, UC)
- Bacterial overgrowth (gi surgery, motility)
- parisitic: giardia
75. Clinical Disinfectants
-
Alcohol cell membranes, __P__roteins not-sporicidal -
Chlorhexidin cell membranes,__C__ytoplasm not-sporicidal -
H202 destructivefreeradicals sporicidal -
Iodine Halogenation sporicidal
76. Gout causing drugs:
URIC ACID secretion reducers:
- Diuretics - loop, thiazide
- Salicylates - low dose
- ACEI
- Cyclosporin
77. Sjogren syndrome: which cellular infiltration?
- Lymphocytic INfiltration around germinal centers
- also normal serous acini
- Salivary gland:

78. OCCULOMOTOR NERVE what fibers in and out?
- OUTER: Parasympathetic N: —– Aneurysmal Compression —– EARLY: Dilated pupil —– LATE: Ptosis, Opthalmoplegia (Down and Out)
- INNER: Deep Extraocular Muscle efferents —– Diabetic (Infarcts first in the deep fibers): Diabetic Opthalmoplegia —– EARLY: Down and Out —– Normal reactive Pupil!
79. common microbes in CF:
- Pseudomonas
- S. Aureus
80. Excocrine Insufficency progressive:
- CF
81. M.Tb pathogenesis:
- tb enters lungs –> alveolar sacs –> Macs eat them –> There is inhibition of Phagosomes and lysosomes –> unchecked growth –> migrate to Lymphnodes –> Macs present antigens (APC) to naive Th0 cells –> Th0 differentiats to Th1 –> Th1 migrates to the site in th elungs –> Th1 secrets INF-gamma and IL2 –> Intracullar killing and granuloma formation
82. Anti-PD1 antibodies / mechanism?
If the tumor cell expresses PD-L1 and B7, it avoids T Cell destruction
- CancerCell–(b7)==(CD28)–TCell
- CancerCell–(MHC)==(TCR)–TCell
- CancerCell–(PDL1)==(PD1)–TCELL
- CancerCell–(B7)==(CTLA-4)–TCell

83. Plasma Cell neoplasm:
- Eccentric Nuclei prominent nucleoli
- Clock face chromatin
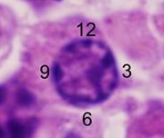
84. Drug reactions with CHELATING agents
- Tetracyclin
- Fluoroquinolones
85. Blood nipple discharge, diagnosis?
- Intraductal papilloma
86. Osteonecrosis of JAW is a s/e of?
- Bisphosphonates!
- commonly used high doses for cancer or oral surgeries
87. Abdomen CT
88. Cold is intra or extra vascular hemolysis?
- INTRAvascular hemolysis
- Infection: Mycoplasma, Hematological Malignancies, IgM
- EAR PINNA
89. WARM Agglutination exampels:
- SLE
- CLL
- Medications/Penicillin? (combs+)
- IgG
90. Calculating Clearance __ === GFR ?; __ === RBF?
- INULIN == GFR (freely filtered, no absorption or secretion) – Amount Excreted == Amount Filtered
- PAH == RPF (freely filtered, some Secretion from tubule – Amount Excreted > Amount Filtered
Estrogen increases or decreases T4?
- Increases T4
- Estrogen Increase –> Inc TBG, Inc Bound-T4 –> Decrease FreeT4 –+> Hypothalamus (TRH) –+> TSH –+> Thyroid T3,T4 –> Increase T4 free level (restored)
Needle shaped cholesterol clefts on micrsocopy?
- AtheroEMBOLIZATION
- clefts are surrounded by multi nucleated giants cells
